|
pyrithiobac-sodium
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; pyrimidinyloxybenzoic analogue
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pyrithiobac-sodium (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
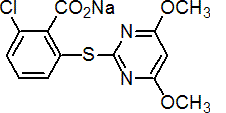
IUPAC name sodium 2-chloro-6-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylthio)benzoate
Chemical Abstracts name sodium 2-chloro-6-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-ylthio)benzoate
CAS RN [123343-16-8] sodium salt; [123342-93-8] parent acid Development codes KIH-2031 (Kumiai); DPX-PE 350 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >93%. Mol. wt. 348.7 M.f. C13H10ClN2NaO4S Form Off white powder at ambient temperature. M.p. 233.8-234.2 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 4.80 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.6 (pH 5), -0.84 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.609 Solubility In water 264 (pH 5), 705 (pH 7), 690 (pH 9), 728 (unbuffered) (all in g/l, 20 °C). In acetone 812, methanol 270 ´ 103, n-hexane 10, dichloromethane 8.38 (all in mg/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable in water (32 d, pH 5-9, 27 °C) and to heat (15 d at 54 °C). pKa 2.34
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered in 1988 by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. Reported by S. Takahashi et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1991, 1, 57-62. Developed jointly by Kumiai, Ihara Chemical Industry Co., Ltd and E. I. du Pont de Nemours Co. Introduced by DuPont in USA in 1995. Patents US 4932999; EP 315889 Manufacturers Ihara/Kumiai
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Selectivity is based on differing rates of metabolism. Mode of action Initial symptoms are cessation of growth and yellowing, followed by necrosis of terminal tissue and death. Uses Control of a wide range of broad-leaved weeds in cotton. Weeds controlled post-emergence, at 40-105 g/ha include Ipomoea spp., Xanthium spp., and Amaranthus spp.; those controlled pre-emergence, at 35-50 g/ha include Amaranthus spp., Sida spinosa, and Abutilon theophrasti. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to cotton when applied as directed. Formulation types SP; SL. Selected products: 'Staple' (DuPont, Kumiai)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Staple Plus' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Details from DuPont.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3300, female rats 3200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.9 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 58.7, female rats 278 mg/kg b.w. daily; (78 w) for male mice 217, female mice 319 mg/kg b.w. daily. Other Non-mutagenic. Non-teratogenic (rats and rabbits). Non-oncogenic (rats). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg b.w. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >930, rainbow trout >1000, sheepshead minnow >145 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >1100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 107 mg/l; NOEC for Selenastrum capricornutum 22.8 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact) >25 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals More than 90% of radiolabelled pyrithiobac-sodium, applied orally and intravenously at 5 mg/kg to rats, was excreted in urine and faeces within 48 h; the major excreted metabolite was the O-desmethyl derivative. Pyrithiobac-sodium applied to hens and goats at 10 ppm diet was also substantially excreted, mostly unchanged, but the O-desmethyl derivative was a significant metabolite; residues in the kidney of both species were £0.06 ppm and were lower in liver, muscle and fat. Plants Amounts of pyrithiobac-sodium in cotton leaves rapidly decreased, following foliar application; at 62 dat, no residues were found; major metabolites found in foliage were the phenol formed by mono-demethylation, and its glucose conjugate. No residues were found in mature cotton seed on lint. Soil/Environment Microbial and photochemical degradation play a major role in degradation in the environment; DT50 in silty soil 60 d. Kd 0.32 (sandy loam), 0.60, 0.38, 0.75 (3 silty loam soils).
|